Installing PrairieLearn Locally on Windows
-
Open PowerShell. Install Ubuntu in WSL 2 using the command
wsl --install -d Ubuntu -
Install Docker Desktop. If you don’t have an account, create one using your UVA email.
-
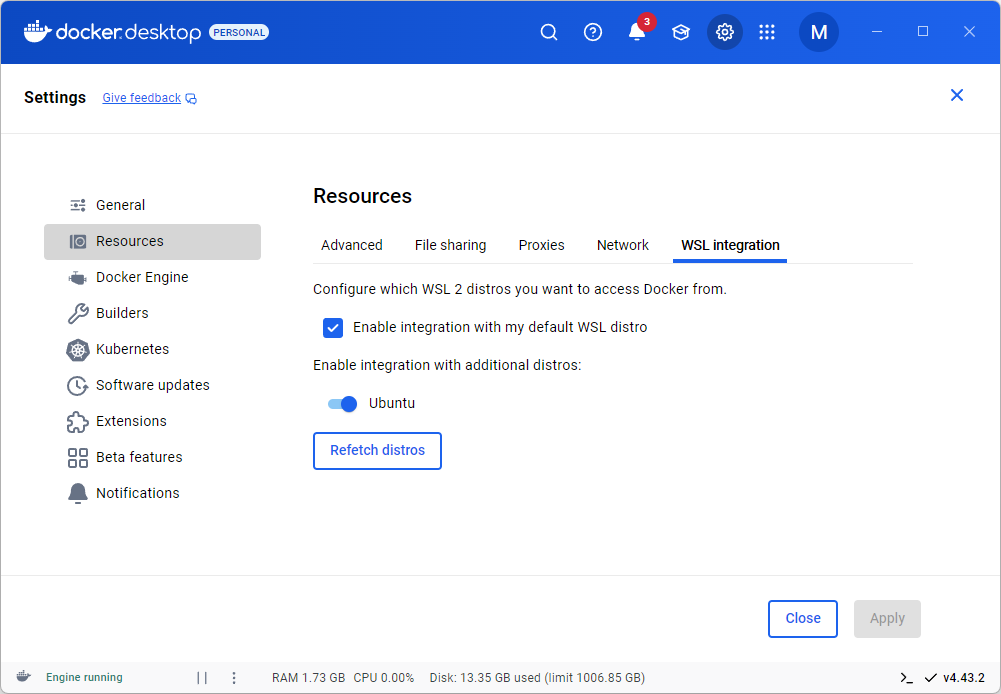
In Docker Desktop, go to Settings (gear icon) > Resourses > WSL integration and ensure the following options are selected:
- Head over to GitHub. Go to Settings > Developer Settings > Personal access tokens > Tokens (classic). Select Generate new token > Generate new token (classic). Fill in the following options:
- Note: PrairieLearn CS2100
- Expiration: Custom > end of the semester (you should create a new token each semester for security)
- Select scopes: Check all the boxes in the “repo” section. All other checkboxes should be left unchecked.
-
Click “Generate token”. Copy the token that appears on screen now and save it somewhere. You will need it later and cannot see it again! If you lose it, you can always create a new token.
-
Go to following GitHub repository: https://github.com/PrairieLearn/pl-virginia-cs2100. This is where all the question, assessment, and course data is stored. If your GitHub account does not have access, please contact Professor Morrison and ask her to add your GitHub username as a collaborator. You need access to this repository to continue.
-
Search for the “Ubuntu” app on your computer and open it. It should launch a terminal window of Ubuntu in WSL2. Run the command
pwdand ensure you are in the/home/[yourusername]directory. If not, navigate to this directory usingcd /home/[yourusername]. If you don’t know your username, run the commandwhoamiand it will tell you. -
Run the command
git clone https://github.com/PrairieLearn/pl-virginia-cs2100.git. Enter your GitHub username when prompted. For your password, paste the token you created earlier. This clones the repository into a new directorypl-virginia-cs2100. -
After cloning the repository, we need to create another folder on the same level as
pl-virginia-cs2100. Ensure your terminal is still located at/home/[yourusername]and run the commandmkdir pl-jobs. This directory will be used to store autograder jobs. Still create this folder even if you aren’t planning to write questions using an autograder. - Run the command:
docker run -it --rm -p 3000:3000 -v "$HOME/pl-virginia-cs2100:/course" -v "$HOME/pl-jobs:/jobs" -e HOST_JOBS_DIR="$HOME/pl-jobs" -v //var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --add-host=host.docker.internal:172.17.0.1 prairielearn/prairielearn(it may take longer the first time)
-
Open your browser and go to http://localhost:3000/. You should now see PrairieLearn running locally!
- Click “Load from disk” on the top right. After it is done, click “Back to previous page”. You should now see CS 2100 as a course with instructor access. When you click on it, it takes you to the course homepage. From here, you’ll probably be using the “Questions” tab the most.
If you are getting an error while loading from disk, you may need to update the PrairieLearn Docker image. In the Ubuntu terminal, run the command:
docker pull prairielearn/prairielearn
Important: When you are finished with your locally running PrairieLearn instance, it is important to shut it down. To do this, go back into your terminal where you launched PrairieLearn and press Ctrl+C. To launch PrairieLearn again, paste the same long command from step 10 into an Ubuntu terminal and go to http://localhost:3000/.
Setting Up VS Code for development
-
Install VS Code if you do not already have it.
-
Install the “WSL” extension in VS Code:
-
Open Ubuntu in your terminal (if you still have it open, you don’t need to relaunch it). Move into the
pl-virginia-cs2100directory using the commandcd /home/[yourusername]/pl-virginia-cs2100/. -
Run the command
code .This will launch a remote VS Code window connected to your local copy of the PrairieLearn course folder. It may take longer the first time.